Project Quality Management: Testing
- jgentr11
- Oct 22, 2021
- 4 min read
Updated: Nov 4, 2021
Introduction
Testing is the act of checking if the product of a project is meeting the quality standards of the team and stakeholders. When working on an agile project the team should use testing along the entire process of creation to better ensure quality of the final product. It is common for teams to only test a product right before shipping in a waterfall approach, but this is not thorough enough for agile and can cause shipping of a product not up to quality. With agile, teams focus on stakeholders requirements and work closely with them to meet those requirements. To prevent teams from not meeting requirements and satisfaction of their users there are many different forms of testing that teams can make use of within each approach:
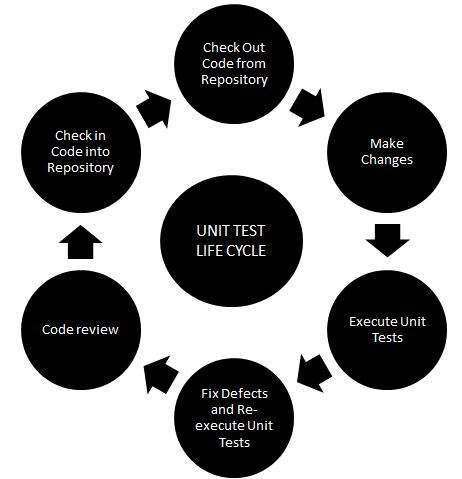
Unit Testing
Tests each individual component to make sure it is as defect-free as possible
In software, individual units of source code
Is used to determine if there are any defects by the developers themselves
Isolates each unit to identify, analyze, and fix defects
Techniques:
Black Box- User interface input and output are tested
White Box- Each functions behavior is tested
Grey Box- Execute tests, risks and assessment methods
In agile:
Uses program fragment to test a certain part of source code
Gives teams the ability to quickly and independently identify errors within certain segments of their code
Done before Integration Testing
Integration Testing
Tests functionally grouped components for performance and reliability
Ensures that subsets of the entire system work together
Strategies:
Big-bang Integration- All units are linked at once, creates a complete system
Top-Down Integration- Used to simulate behavior of lower-level modules that have not been implemented
Bottom-Up Integration- Lower levels are tested individually, then the components they rely on are tested
Hybrid integration- Use both techniques of Top-Down and Bottom-Up together
In agile:
Integration testing is a core part agile methodology
Allows for teams to see if different components of hardware and software interact in a predicted manner
Occurs between Unit and System Testing
System Testing
Tests the entire system as one entity to ensure that the whole system is working correctly
Measured against specified requirements
Tested from an end-to-end perspective
Typically carried out by a team that is separate from the developing team
Ensures that the test is unbiased
Types of System Tests:

User Acceptance Testing
An independent test performed by the end user before accepting the final product delivery
Focus on fit of the system to the business or the requirements instead of technical
It is context dependent and will change for each product specifically
In Agile:
Also called Acceptance test-driven development
Gives users test cases to complete
Allows for development team to directly see how users interact with their product and get feedback if their product is meeting the users requirements
Supplemented by Behavior-driven development that adds the business outcomes and if the tests meet those outcomes

Other Testing
Alpha- Testing done a developers site by internal members of the company that are not part of the development team
Beta- Testing done be end users to validate usability, functionality, compatibility, and reliability
Performance- Non-functional Testing to test responsiveness and stability under various workloads
Scalability- Tests the systems ability to grow with workload, concurrent users, and database size
Exploratory- The process and loop of test design, test execution, analyzing, and learning that allows for users to interact and explore the product without any guidelines or test cases
Allows for users to experience the website as if they came across it while searching the web
Conclusion
All these testing techniques and methods are used to “iron out” errors and defects that happen in the creation process whether it is from the developers themselves, inherent problems with the system, or other factors. With running rigorous tests comes the assurance of quality in the product that a development team is providing to their end users and stakeholders. Another benefit from this is reduction of time and cost as teams will not get to the end of a project and realize the errors in the product they have created and must rework the entire system to meet the quality standards. Testing is the best way for development teams to assure that the product they are putting out will reach the user acceptance criteria and the requirements put in place by them to satisfy end users.
Testing is an important part of agile project management. Testing is done often and early in the agile process for teams to communicate with stakeholders on what needs to be changed and to address those changes in their project. In agile, testing is integrated throughout the process, continuously and not only just before deployment. This is because the goal is to deliver value and with agile to do so means that you need to work closely with stakeholders to deliver a product that meets their requirements. With agile there are three other types of testing to consider acceptance test-driven, behavior-driven, and exploratory. Acceptance test-driven uses test cases to have users work through a process of a functional prototype. This allows for teams to see directly what users want from their product. Behavior-drive is used to enhance Acceptance test-driven development as it adds the identification of correct outcomes and performs tests based on them. Lastly, exploratory is the process of test design, test execution, analyze, and learn. These steps are repeated by testers. This is meant for testers to get a feel for the product with a guide of test cases, but instead how they would enter and use the product when they find it own their own. This all shows the importance and focus of testing within the agile approach and how project managers and team members should be knowledgeable on the different forms of testing they can implement to their product development to better meet the needs and requirements of their users.
References:
Global App Testing (Spa Worldwide Limited) is a company registered in England under no. 07606704. (2021). Best practices for agile testing. Best Practices for Agile Testing. Retrieved November 4, 2021, from https://www.globalapptesting.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-agile-testing.
Schwalbe, K. (2019). Information technology project management (9th ed.). Cengage.
Software testing dictionary. (n.d.). Retrieved October 22, 2021, from https://www.tutorialspoint.com/software_testing_dictionary/index.htm.




Comments